Few can rival the charm and performance of the 2008 Mazda 3 when it comes to reliable compact cars. With its sporty design and agile handling, this beloved hatchback has captured the hearts of drivers worldwide. But beneath its sleek exterior lies a hidden hero—the 2008 Mazda 3 alternator—often overlooked yet pivotal in keeping your vehicle running smoothly. Join us as we dive deep into the mystique surrounding this electrical powerhouse! From understanding its crucial role in your car's performance to tips for maintenance and troubleshooting common issues, we’ll illuminate everything you need to know about ensuring your Mazda 3 stays charged up and ready for adventure.
Introduction to the 2008 Mazda 3 and its Alternator
Regarding the 2008 Mazda 3, fans celebrate its sleek design and spirited performance. But hidden under that stylish hood is a crucial component that often gets overlooked—the alternator. This small yet mighty device plays a significant role in keeping your car running smoothly and efficiently. Understanding its function can save you from unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. So buckle up as we dive into the fascinating world of alternators, unravelling their mystique specifically for your beloved Mazda 3!
The Purpose of a 2009 Mazda 3 alternator in a Car
The 2009 Mazda 3 alternator is crucial to your car's electrical system. It transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating power while the engine runs. This component charges the battery and power accessories like lights, radio, and air conditioning. Without it, these systems would quickly drain your battery, leaving you stranded.
Unlike a generator that requires manual intervention to start producing electricity, an alternator works seamlessly as soon as the engine fires up. It maintains an optimal voltage level to ensure all electrical components function smoothly.
Moreover, modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic systems. The alternator ensures they receive consistent power without fluctuation. This stability prevents potential damage from overloading or underpowering delicate electronics. Every time you drive your Mazda 3, remember that it's the alternator keeping everything running harmoniously beneath the hood.
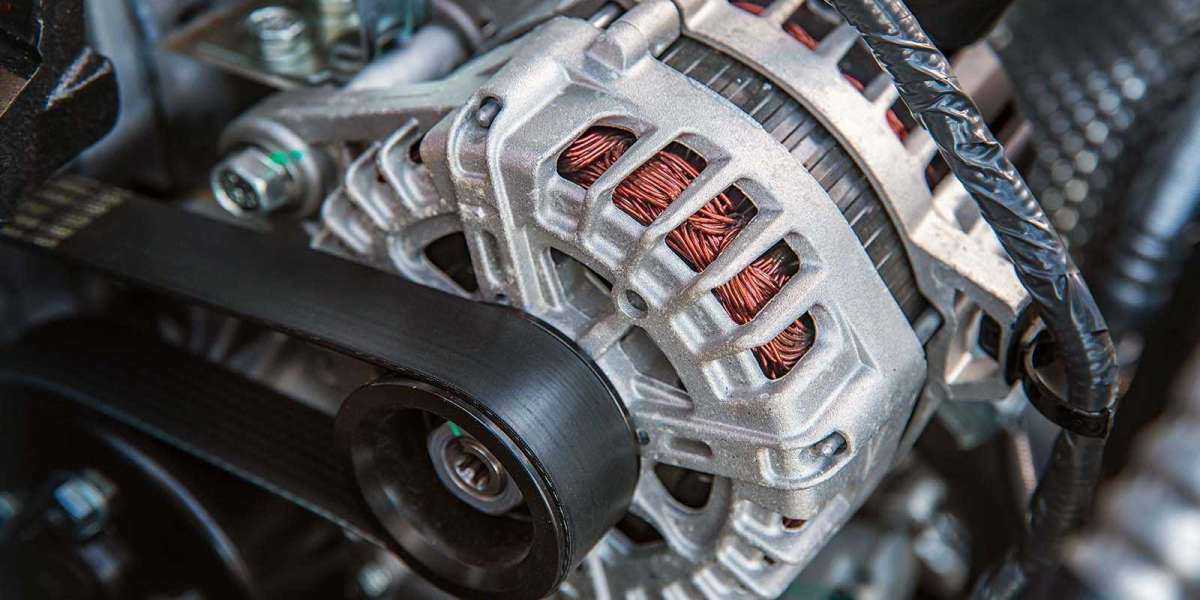
Understanding the Different Parts of the 2010 Mazda 3 alternator
The alternator is a crucial component of the Mazda 3. It is responsible for keeping the electrical system running smoothly and powering various devices such as the headlights, air conditioning, and radio. If you're experiencing issues with your Mazda's electrical system, it's essential to understand the different parts of the 2010 Mazda 3 alternator to diagnose and address any problems appropriately.
1.The Rotor
The rotor is the heart of the alternator and creates a magnetic field that induces an electrical current in the stator windings. It consists of a shaft, pulley, and copper wire winding that rotates inside stationary magnets.
2. Stator Windings
The stator windings are stationary copper wires that surround the rotor and produce electricity when exposed to an alternating magnetic field created by the spinning rotor.
3. Diode Rectifier
The diode rectifier converts alternating current (AC) produced by the stator into direct current (DC), necessary for charging the battery and powering electronic devices in your car.
4. Voltage Regulator
As its name suggests, this component regulates how much voltage the alternator sends to keep your battery charged properly. It also protects other electrical components in your car from damage by high-voltage spikes.
5. Bearings
The bearings support and allow smooth rotation of both ends of the rotor shaft while under load caused by belt tension, ensuring the alternator's efficient operation.
6. Pulley
This part helps transfer power from a belt attached to your engine crankshaft to rotate or spin within speed limits determined by gears inside it.
7. Slip Rings/Brushes
These two components work together to transfer power from rotating parts (rotors) to stationary ones(stators).
Signs of a Failing Alternator in a 2008 Mazda 3
A failing alternator can spell trouble for your 2008 Mazda 3. Recognising the early signs is crucial to avoid being stranded.
First, pay attention to dashboard warning lights. If the battery or alternator light flickers on, it’s a red flag that something isn’t right. Strange noises are another indicator. A grating or whining sound could mean the alternator's bearings are wearing out.
You might also notice dimming headlights and electrical issues. If your lights appear weak or fluctuate in brightness, it’s time to investigate further. Lastly, your alternator may not be charging properly if you experience frequent dead batteries despite recent replacements. Each of these signs warrants immediate attention to keep your Mazda performing at its best.
Common Issues with the Alternator in a 2008 Mazda 3
The alternator in the 2008 Mazda 3 can face several common issues drivers should be aware of. One frequent problem is a loose or worn serpentine belt, which can cause intermittent electrical failures. If you notice strange noises from the engine bay, it might be time to inspect this component.
Another issue involves poor connections at the battery or wiring harness. Corrosion can build up over time, leading to weak power output and complete failure.
Additionally, many owners are concerned about overheating. High temperatures can damage internal components and significantly reduce efficiency. Lastly, check the warning lights on your dashboard. A flickering battery light could indicate underlying alternator problems that require immediate attention before they escalate into more serious repairs.
How to Test and Replace the 2011 Mazda 3 alternator
Testing the 2011 Mazda 3 alternator is straightforward. Start by checking the battery voltage with a multimeter. When not running, a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
Next, start the engine and measure again while it runs. Your alternator functions correctly if the reading jumps between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. If you suspect it’s time for a replacement, disconnect the negative terminal from your battery first for safety. Then, remove any belts connected to the alternator and unbolt it from its mount.
Carefully remove the old unit and install the new one in reverse order. Make sure everything is tightly secured before reconnecting your battery terminal and testing once more to ensure the proper functionality of your newly installed alternator.
Tips for Maintaining Your 2012 Mazda 3 Alternator
The alternator is a crucial component of your Mazda 3's electrical system, and it is responsible for keeping the battery charged and powering various electrical systems in your car. As such, it is essential to properly maintain this vital part to ensure your vehicle's smooth functioning. Here are some tips for keeping the 2012 Mazda 3 alternator:
1.Regularly inspect the alternator
It is essential to regularly check the condition of your alternator to identify any potential issues before they become significant problems. Look for signs of wear and tear such as loose connections, frayed wires, or corrosion on the terminals.
2. Keep it clean
Dirt and debris can build up on the alternator's surface and hinder its performance. Make sure to clean it regularly with a soft cloth or brush. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the delicate components.
3. Check belt tension
The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine crankshaft pulley. Over time, this belt can become worn or loose, causing slipping and reduced output from the alternator. It is essential to regularly check and adjust the belt tension according to the manufacturer's specifications.
4. Test voltage output
If you notice any issues with your car's electrical systems, such as dimming headlights or slow power windows, it may be a sign of low voltage output from your alternator. You can test this using a multimeter while the car's engine runs at idle speed.
Following these tips, you can keep your 2012 Mazda 3 alternator in top condition and avoid any unexpected breakdowns. Remember that a well-maintained alternator ensures smooth functioning of your car and contributes to its overall longevity. If you have any doubts or concerns about your alternator, it is always best to consult a professional mechanic for expert advice and assistance.
Upgrading Your 2013 Mazda 3 alternator: Is it Worth it?
If you own a 2013 Mazda 3, you may have noticed that your 2013 Mazda 3 alternator is starting to show signs of wear and tear. Over time, the alternator in any car can become less efficient and eventually fail altogether. Many Mazda 3 owners wonder whether upgrading their alternator is worth the investment or if they should stick with the original one.
To answer this question, it's important to understand how your car's alternator works and why it's such an integral part of your vehicle's power system. The alternator is responsible for converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy that powers your car's electronic components, including lights, radio, and air conditioning. Without a functioning alternator, your battery would quickly drain and leave you stranded on the side of the road.
So why would someone want to upgrade their stock alternator? There are a few reasons why this might be beneficial. Firstly, an upgraded alternator can provide more power output than a stock one. This means you'll have more electricity to run additional accessories or upgrades like high-powered stereo systems or aftermarket lighting.
Another reason some Mazda 3 owners upgrade their alternators is for improved reliability. Aftermarket performance alternators are often built with higher-quality materials and better construction methods than original ones, making them less likely to fail or malfunction.
Conclusion
Keeping your Mazda 3 running smoothly relies heavily on understanding and maintaining its alternator. This vital component powers the electrical system and charges the battery, ensuring your vehicle functions optimally. Regular checks for signs of wear or malfunction can save you from unexpected breakdowns. If you notice dimming lights, strange noises, or warning indicators on your dashboard, it’s time to investigate further. Familiarising yourself with the 2008 Mazda 3 alternator's different parts will help diagnose issues more effectively. Testing and replacing an alternator might seem daunting initially, but with some know-how and preparation, it can be tackled as a DIY project. Maintain clean connections and monitor battery health to extend its lifespan.
FAQs
Q: What is an alternator?
A: An alternator is a vital component of a vehicle's charging system. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy to power various electrical systems in the car.
Q: How does an alternator work?
A: The alternator uses a series of rotating belts and pulleys connected to the engine crankshaft to spin a magnet inside copper wire coils. This creates an alternating current (AC) converted into direct current (DC) by rectifiers and sent out as electricity to charge the battery and power other electrical components.
Q: How often should I get my 2008 Mazda 3 alternator checked?
A: It is recommended that your2008 Mazda 3 alternator be checked every 50,000 miles or during routine maintenance checks. However, if you notice any warning signs, such as dimming headlights or difficulty starting your car, it's best to get it checked immediately.
Related Business Listings |